Inhalt:

Aufgaben
Durch den Bundesrat sind die Bundesländer an der Gesetzgebung des Bundes beteiligt (zum Beispiel Artikel 76 I GG).
Der Bundesrat ist ferner an der Verwaltung des Bundes beteiligt (zum Beispiel Artikel 84 II, 85 II GG).
Er kontrolliert die Regierung (zum Beispiel Artikel 53 GG) und wirkt bei der Bestellung anderer Bundesorgane mit (zum Beispiel Artikel 94 I S 2 GG).
Zusammensetzung
Der Bundesrat besteht momentan aus insgesamt 69 Mitgliedern.
Die Zahl der Stimmen und damit der Mitglieder pro Bundesland richtet sich nach der Einwohnerzahl des jeweiligen Bundeslandes (Artikel 51 II GG). Baden-Württemberg hat mehr als 7 Millionen Einwohner und daher im Bundesrat 6 Stimmen.
Artikel 51 II
Jedes Land hat mindestens drei Stimmen, Länder mit mehr als zwei Millionen Einwohnern haben vier, Länder mit mehr als sechs Millionen Einwohnern fünf, Länder mit mehr als sieben Millionen Einwohnern sechs Stimmen.
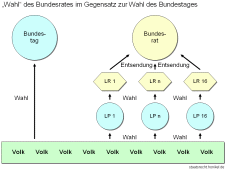
Die Bundesratsmitglieder werden nicht wie die Bundestagsabgeordneten vom Volk gewählt, sondern sind Mitglieder der Landesregierungen der verschiedenen Bundesländer (zum Beispiel Ministerpräsidenten, Minister). Sie werden von den Landesregierungen in den Bundesrat entsandt.
Artikel 51 I
Der Bundesrat besteht aus Mitgliedern der Regierungen der Länder, die sie bestellen und abberufen. Sie können durch andere Mitglieder ihrer Regierungen vertreten werden.
Die Bundesratsmitglieder sind bei der Abgabe ihrer Stimmen im Gegensatz zu den Bundestagsabgeordneten nicht frei und unabhängig, sondern an Weisungen ihrer jeweiligen Landesregierung gebunden (imperatives Mandat, Artikel 51 I GG, „...die sie bestellen und abberufen...”).
Sie dürfen nicht gleichzeitig dem Bundestag angehören (Inkompatibilität).
Amtsdauer
Der Bundesrat hat im Gegensatz zum Bundestag keine Legislaturperiode. Er ist ein so genanntes „ewiges Bundesorgan”. Ein Teil der Bundesratsmitglieder wechselt dann, wenn in einem der Bundesländer eine neue Landesregierung gewählt wird.
Beschlussfassung
Der Bundesrat (Bundesratsplenum) fasst, im Gegensatz zum Bundestag, seine Beschlüsse in der Regel mit absoluter Mehrheit, das heißt mit der Mehrheit seiner gesetzlichen Stimmen (Artikel 52 III S 1 GG).
Bei grundgesetzändernden Gesetzen ist eine 2/3-Mehrheit im Bundesrat erforderlich (Artikel 79 II GG, Artikel 61 I GG).
Beschlussfähig ist der Bundesrat, wenn die Mehrheit seiner Stimmen vertreten ist (§ 28 Geschäftsordnung des Bundesrates [GOBR]).
Bei der Abstimmung können die Stimmen eines Landes nur einheitlich und nur durch anwesende Mitglieder oder deren Vertreter, also durch Regierungsmitglieder, abgegeben werden (Artikel 51 III S 2 GG). Ein Mitglied kann stellvertretend alle Stimmen seines Landes abgeben.
Artikel 51 III
Jedes Land kann so viele Mitglieder entsenden, wie es Stimmen hat. Die Stimmen eines Landes können nur einheitlich und nur durch anwesende Mitglieder oder deren Vertreter abgegeben werden.
Organisation
Der Bundesrat wählt turnusmäßig einen Ministerpräsidenten jeweils für ein Jahr zu seinem Präsidenten (Artikel 52 I GG).
Der Bundesratspräsident beruft den Bundesrat ein und führt den Vorsitz bei den Sitzungen. Er ist außerdem Stellvertreter des Bundespräsidenten (Artikel 57 GG).
Neben dem Präsidenten wählt der Bundesrat drei Vizepräsidenten, die mit dem Präsidenten das Präsidium bilden. Wie auch der Bundestag bildet der Bundesrat Ausschüsse zur politischen Sacharbeit (Artikel 52 IV GG). Für Angelegenheiten der EU hat der Bundesrat eine Europakammer gebildet, die seine Mitwirkungsrechte wahrnimmt. Deren Beschlüsse gelten als die des Bundesrates (Artikel 52 III a GG).
Die Sitzungen des Bundesrates sind grundsätzlich öffentlich, die Öffentlichkeit kann jedoch gegebenenfalls ausgeschlossen werden (Artikel 52 III GG).