Inhalt:
Überblick
Begriff
Grundrechte sind grundlegende, individuelle Rechte, die in der Verfassung genannt und garantiert werden.
Sie binden unmittelbar den Staat (Artikel 1 III GG) und begrenzen die Macht des Staates gegenüber dem Einzelnen. Der Staat darf nicht beliebig über seine Bürger verfügen. Grundrechte wirken also vor allem als Abwehrrechte des Bürgers gegen den Staat.
Mittelbar wirken die Grundrechte als „objektive Wertordnung” auch auf die Rechtsbeziehungen des Privatrechts. Zum Besipiel müssen die Generalklauseln des BGB grundrechtskonform ausgelegt werden. Diese mittelbare Drittwirkung ist jedoch schwächer als die unmittelbare Bindung des Staates an die Grundrechte.
Fundstellen
Die Grundrechte finden Sie im Grundrechtekatalog der Artikel 1 bis 19 GG.
Außerdem sind an anderen Stellen des Grundgesetzes, zum Beispiel im Artikel 33 GG, Regelungen enthalten, die den Grundrechten gleichgestellt sind. Eine abschließende Aufzählung dieser grundrechtsgleichen Rechte befindet sich im Artikel 93 I Nr. 4 a GG.
Artikel 93 I Nr. 4a
[Das Bundesverfassungsgericht entscheidet]...
über Verfassungsbeschwerden, die von jedermann mit der Behauptung erhoben werden können, durch die öffentliche Gewalt in einem seiner Grundrechte oder in einem seiner in Artikel 20 Absatz 4, 33, 38, 101, 103 und 104 enthaltenen Rechte verletzt zu sein;
Grundrechtsträger (Anspruchsberechtigte)
Auf Grundrechte können sich alle natürlichen Personen berufen. Außerdem können sich alle inländischen juristischen Personen des privaten Rechts auf sie berufen, soweit Grundrechte auf sie sinnvoll angewandt werden können (Artikel 19 III GG).
Anwendbare Grundrechte sind zum Beispiel die Artikel 3, 9 und 10 GG. Nicht anwendbare Grundrechte sind zum Beispiel die Artikel 1 I, 2 II und 3 II GG, also menschenbezogene Grundrechte, deren Anwendung bei juristischen Personen keinen Sinn ergibt.
Gemeinden als juristische Personen des öffentlichen Rechts können sich nicht auf Grundrechte berufen, sondern sind an Grundrechte gebunden.
Grundrechtsmündigkeit
Unter Grundrechtsmündigkeit versteht man die Fähigkeit natürlicher Personen ihre Grundrechte geltend machen zu können. Grundrechtsmündig sind selbständige Volljährige und Minderjährige, wenn sie die geistige Reife und Einsichtsfähigkeit besitzen. Auf Altersstufen wie im BGB kommt es in der Regel nicht an.
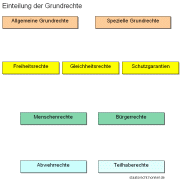
Einteilung der Grundrechte
Die Grundrechte können nach verschiedenen Kriterien eingeteilt werden. Folgende Einteilungen sind im Staatsrecht gebräuchlich:
Nach dem Schutzzweck
a) Freiheitsrechte
Freiheitsrechte legen einen bestimmten Handlungsbereich fest. Innerhalb dieses Bereichs kann der Einzelne so handeln, wie er will (zum Beispiel Artikel 8, 9, 2 I GG).
b) Gleichheitsrechte
Gleichheitsrechte regeln, dass im Wesentlichen gleiche Sachverhalte rechtlich gleich und im Wesentlichen ungleiche Sachverhalte rechtlich ungleich zu behandeln sind (zum Beispiel Artikel 6 V, 3 I GG).
Unterschiede dürfen nur dort gemacht werden, wo sie sachlich begründet sind (Willkürverbot). Außerdem gilt: Keine Gleichbehandlung im Unrecht.
c) Institutionsgarantien und Verfahrensgrundrechte
Zusätzlich zu den Grundrechten für Einzelne gibt es auch Institutionsgarantien, zum Beispiel Ehe und Familie (Artikel 6 GG) oder Presse (Artikel 5 I GG) und Verfahrensgrundrechte (zum Beispiel Artikel 19 IV, 101 GG).
Nach der Wirkungsbreite
a) Spezielle Grundrechte
Diese Grundrechte gelten für eng umgrenzte Tatbestände, zum Beispiel Artikel 12 GG für Berufe oder Artikel 6 V GG für uneheliche Kinder.
b) Allgemeine Grundrechte
Diese Grundrechte (Artikel 2 I GG – Freiheitsgrundrechte und 3 I GG – Gleichheitsgrundrechte) gelten für eine Vielzahl von Tatbeständen.
In einem Grundrechtsfall werden zunächst die speziellen Grundrechte geprüft. Erst dann, wenn kein vom Handlungsbereich passendes Grundrecht gefunden wird, kommt ein allgemeines Grundrecht (Freiheits- oder Gleichheitsgrundrecht) als „Auffanggrundrecht” in Betracht. Dieses wird also subsidiär (nachrangig) geprüft. Eine gleichzeitige Anwendung von speziellen und allgemeinen Grundrechten für denselben Tatbestand darf nicht erfolgen.
Nach dem geschützten Personenkreis
a) Menschenrechte („Jedermannsrechte”)
Menschenrechte gelten für jeden, unabhängig von der jeweiligen Staatsangehörigkeit („Jeder hat ...”).
b) Bürgerrechte
Bürgerrechte gelten nur für Personen mit deutscher Staatsangehörigkeit (Artikel 16 und 116 GG) („Jeder Deutsche...”).
Hinweis:
Der Begriff „Menschenrechte” wird auch in dem Sinn gebraucht, dass es sich bei Menschenrechten um jedem Menschen von Natur aus zustehende Rechte handelt. Im Gegensatz dazu handelt es sich bei Grundrechten um Rechte, die vom Staat verliehen werden.
Nach der Zielrichtung
a) Abwehrrechte
Die Grundrechte als Abwehrrechte schützen die Bürger gegen Eingriffe des Staates in ihre Rechtssphäre.
b) Leistungs- oder Teilhaberrechte
Grundrechte können in seltenen Fällen auch ein Recht auf staatliche Leistung beinhalten, zum Beispiel das Recht auf Sozialhilfe (Artikel 1 I in Verbindung mit Artikel 2 II S 1 in Verbindung mit Artikel 20 I GG).
Einschränkung der Grundrechte
In einer Gemeinschaft, wie sie in einem Staat naturgemäß besteht, würde eine freie, uneingeschränkte Berufung auf Grundrechte durch die verschiedenen Menschen dazu führen, dass sie sich ständig gegenseitig behindern, da sie sich in ihren Zielen voneinander unterscheiden („Grundrechtekollision”). Beschränkungen sind also zwingend notwendig.

Um zu verhindern, dass durch diese Beschränkungen die Grundrechte faktisch außer Kraft gesetzt werden, sind die Beschränkungen aber ausschließlich innerhalb festgelegter Grenzen zulässig.
Bei allen Beschränkungen darf der Wesensgehalt, die Kernaussage eines Grundrechts, nicht angetastet werden, außerdem muss die Beschränkung verhältnismäßig sein. Die Beschränkungen dürfen ferner nur durch die folgenden drei Schrankentypen erfolgen:
Verfassungsunmittelbare Schranken
Verfassungsunmittelbare Schranken sind unmittelbare Begrenzungen eines Grundrechts direkt im Grundgesetztext, zum Beispiel Artikel 2 I, 5 II, 8 I, 9 II GG.
Gesetzesvorbehaltsschranken
Ein Grundrecht wird durch oder aufgrund eines Gesetzes eingeschränkt (vom Grundgesetz wird auf ein Gesetz verwiesen), zum Beispiel Artikel 4 III, 8 II, 13 III GG.
Gesetzesvorbehaltsschranken können weiter eingeteilt werden in Regelungsvorbehalte (zum Beispiel Artikel 12 I GG) und Eingriffsvorbehalte (zum Beispiel 13 II GG).
Verfassungsimmanente Schranken
Verfassungsimmanente Schranken sind Schranken, die sich aus dem System des Grundgesetzes mit gleichrangigen Grundrechten ergeben. Immer dann, wenn Grundrechte gegenseitig in Konkurrenz treten, muss im konkreten Einzelfall entschieden werden, wie weit die beteiligten Grundrechte jeweils eingeschränkt werden müssen.
Verfassungsimmanente Schranken gelten für alle Grundrechte. Also auch für die, die von ihrem Wortlaut her schrankenlos erscheinen (zum Beispiel Artikel 3 I, 4 I GG).
Einzige Ausnahme ist der Artikel 1 I GG. Er kann nie eingeschränkt werden.
Jede Einschränkung setzt im übrigen ein formell und materiell rechtmäßiges Gesetz voraus. Durch rechtswidrige Gesetze können Grundrechte nicht eingeschränkt werden.
Schutz der Grundrechte
Aufgrund der Erfahrungen im Dritten Reich wurden die Grundrechte umfassend gegen zu weit gehende Änderungen geschützt:
Wesensgehaltsgarantie (Artikel 19 II GG)
Der Wesensgehalt eines Grundrechts ist die Kernaussage, die das Grundrecht trifft. Dieser darf niemals eingeschränkt werden.
Zitiergebot (Artikel 19 I S 2 GG)
Wenn ein Grundrecht eingeschränkt werden soll, dann muss in der Einschränkung das Grundrecht ausdrücklich genannt werden.
Ewigkeitsklausel (Artikel 79 III GG)
Die Ewigkeitsklausel schützt grundlegende Entscheidungen, die das Grundgesetz trifft, zum Beispiel den Schutz der Würde des Menschen (Artikel 1 I GG) vor jedem legalen Zugriff.
Artikel 79 III
Eine Änderung dieses Grundgesetzes, durch welche die Gliederung des Bundes in Länder, die grundsätzliche Mitwirkung der Länder bei der Gesetzgebung oder die in den Artikeln 1 und 20 niedergelegten Grundsätze berührt werden, ist unzulässig.
Grundrechtsmissbrauch (Artikel 18 GG)
Wenn die Grundrechte zum Kampf gegen die freiheitlich demokratische Grundordnung missbraucht werden, können sie aberkannt werden („sie sind verwirkt”). Diese Verwirkung kann ausschließlich durch das Bundesverfassungsgericht ausgesprochen werden.
Rechtsschutz bei Grundrechtsverletzungen
Grundrechte sind nach Artikel 1 III GG unmittelbar geltendes Recht. Grundrechtsverletzungen können daher über den normalen Rechtsweg (Widerspruch, Klage) geltend gemacht werden. Außerdem kann bei Grundrechtsverletzungen jeder eine Verfassungsbeschwerde beim Bundesverfassungsgericht einreichen (Artikel 19 IV in Verbindung mit 93 I Nr. 4 a GG). In der Regel muss dabei jedoch vorher der übliche Rechtsweg eingehalten werden.
Artikel 1 III
Die nachfolgenden Grundrechte binden Gesetzgebung, vollziehende Gewalt und Rechtsprechung als unmittelbar geltendes Recht.
Artikel 19 IV
Wird jemand durch die öffentliche Gewalt in seinen Rechten verletzt, so steht ihm der Rechtsweg offen. Soweit eine andere Zuständigkeit nicht begründet ist, ist der ordentliche Rechtsweg gegeben. Artikel 10 Absatz 2 Satz 2 bleibt unberührt.
Artikel 93 I Nr. 4a
über Verfassungsbeschwerden, die von jedermann mit der Behauptung erhoben werden können, durch die öffentliche Gewalt in einem seiner Grundrechte oder in einem seiner in Artikel 20 Absatz 4, 33, 38, 101, 103 und 104 enthaltenen Rechte verletzt zu sein
Prüfungsschema für Grundrechtsfälle (Freiheitsrechte)
- Normbereich / Schutzbereich (Sachlicher Bereich für den das Grundrecht gilt)
- Tatbestand
- Sachverhaltssubsumption mit Definition der unbestimmten Rechtsbegriffe des Grundgesetztextes
- Feststellung eines Eingriffs
- Schrankenbereich (Ist das Grundrecht durch einen der drei möglichen Schrankentypen wirksam eingeschränkt?)
- Verfassungsunmittelbare Schranke
- Gesetzesvorbehalt
- Verfassungsimmanente Schranke
- Schranken - Schranken - Bereich (Ist die Einschränkung unverhältnismäßig? Ist der Wesensgehalt eines Grundrechts angetastet? Wenn ja, ist das betreffende Grundrecht verletzt.)
- Güterabwägungsprinzip
- Verhältnismäßigkeitsgrundsatz
- Wechselwirkungstheorie
- Wesensgehaltgarantie
Links zu Grundrechten
- Amnesty International
- Forum Menschenrechte
- Friedenskooperative - Komitee für Grundrechte und Demokratie
- Humanistische Union