Inhalt:

Aufgaben
Das Bundesverfassungsgericht wacht darüber, dass die Organe der Legislative und der Exekutive die Verfassung beachten und einhalten. Das Bundesverfassungsgericht schützt also die Verfassung („Hüter der Verfassung”).
Außerdem interpretiert das Bundesverfassungsgericht die Verfassung. Diese ist (notwendigerweise) allgemein und offen formuliert und muss demnach ständig neu ausgelegt werden.
Es ist in gewisser Weise das höchste Gericht der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Seine Entscheidungen sind für alle verbindlich. Gegen sie sind keine Rechtsbehelfe möglich.
Das Bundesverfassungsgericht hat seinen Sitz in Karlsruhe.
Zusammensetzung und Wahl
Das Bundesverfassungsgericht besteht aus zwei Senaten mit je 8 Richtern. Der Bundestag und der Bundesrat wählen jeweils mit Zweidrittelmehrheit die Hälfte der Richter beider Senate (Artikel 94 I GG).
Artikel 94 I
Das Bundesverfassungsgericht besteht aus Bundesrichtern und anderen Mitgliedern. Die Mitglieder des Bundesverfassungsgerichtes werden je zur Hälfte vom Bundestage und vom Bundesrate gewählt. Sie dürfen weder dem Bundestage, dem Bundesrate, der Bundesregierung noch entsprechenden Organen eines Landes angehören.
Wählbar sind Bundesrichter sowie Personen mit der Befähigung zum Richteramt, also mit beiden juristischen Examen. Sie müssen 40 Jahre oder älter sein und das passive Bundestagswahlrecht besitzen. Die Mitglieder des Bundesverfassungsgerichts dürfen weder Organen der Legislative noch Organen der Exekutive des Bundes oder der Länder angehören.
§ 3 BVerfGG
(1) Die Richter müssen das 40. Lebensjahr vollendet haben, zum Bundestag wählbar sein und sich schriftlich bereit erklärt haben, Mitglied des Bundesverfassungsgerichts zu werden.
Amtsdauer
Die Amtsdauer der Richter des Bundesverfassungsgerichts beträgt 12 Jahre (jedoch maximal bis zum Erreichen einer Altersgrenze von 68 Jahren). Eine erneute Wahl ist ausgeschlossen.
§ 4 BVerfGG
(1) Die Amtszeit der Richter dauert zwölf Jahre, längstens bis zur Altersgrenze.
(2) Eine anschließende oder spätere Wiederwahl der Richter ist ausgeschlossen.
(3) Altersgrenze ist das Ende des Monats, in dem der Richter das 68. Lebensjahr vollendet.
Zuständigkeit
Seine Zuständigkeit ist vor allem in den Artikel 93 und 100 GG geregelt. Das Bundesverfassungsgericht wird nur auf Antrag tätig. Ob das Bundesverfassungsgericht einen Antrag annimmt oder nicht, entscheidet es selbst.
Klagearten
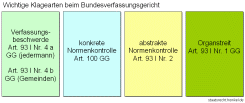
Überblick
Verfassungsbeschwerde
Verfassungsbeschwerden können nach Artikel 93 I Nr.4a GG von jedem mit der Behauptung erhoben werden, durch den Staat in einem Grundrecht verletzt worden zu sein.
Diese Verletzung kann zum Beispiel durch einen Verwaltungsakt oder ein Gerichtsurteil erfolgen. Eine Verfassungsbeschwerde kann jedoch in der Regel erst dann eingelegt werden, wenn der Rechtsweg ausgeschöpft ist.
Verfassungsbeschwerden können ferner nach Artikel 93 I Nr. 4b GG von Gemeinden (Kommunen) und Gemeindeverbänden wegen Verletzung des Selbstverwaltungsrechts der Gemeinden aus Artikel 28 II GG erhoben werden.
Artikel 93 I
[Das Bundesverfassungsgericht entscheidet]...
4a. über Verfassungsbeschwerden, die von jedermann mit der Behauptung erhoben werden können, durch die öffentliche Gewalt in einem seiner Grundrechte oder in einem seiner in Artikel 20 Absatz 4, 33, 38, 101, 103 und 104 enthaltenen Rechte verletzt zu sein;
4b. über Verfassungsbeschwerden von Gemeinden und Gemeindeverbänden wegen Verletzung des Rechts auf Selbstverwaltung nach Artikel 28 durch ein Gesetz, bei Landesgesetzen jedoch nur, soweit nicht Beschwerde beim Landesverfassungsgericht erhoben werden kann;
Konkrete Normenkontrolle (Artikel 100 GG)
Wenn ein Gericht bei einem konkreten, aktuell verhandelten Fall, der Meinung ist, dass das dabei anzuwendende Recht nicht mit dem Grundgesetz vereinbar ist, dann muss dieses Gericht das laufende Verfahren unterbrechen und eine Entscheidung des Bundesverfassungsgerichts abwarten.
Abstrakte Normenkontrolle (Artikel 93 I Nr. 2 GG)
Das Bundesverfassungsgericht prüft hier auf Antrag der Bundesregierung, einer Landesregierung oder mindestens eines Viertels der Mitglieder des Bundestages, ob Bundes- oder Landesrecht unabhängig von einem konkreten Fall mit dem Grundgesetz vereinbar ist.
Organstreit (Artikel 93 I Nr. 1 GG)
Bei Verfassungsstreitigkeiten zwischen den obersten Bundesorganen entscheidet das Bundesverfassungsgericht.
Parteiverbote (Artikel 21 GG)
Wenn Parteien gegen die freiheitlich demokratische Grundordnung verstoßen, dann können sie vom Bundesverfassungsgericht verboten werden. Die Tatsache, dass Parteien im Gegensatz zu anderen Vereinigungen, nur vom Bundesverfassungsgericht verboten werden können wird als „Parteienprivileg” bezeichnet.
Kompetenzprobleme Bund - Länder (Artikel 93 I Nr. 3 und 4 GG)
Wenn die verschiedenen Bundesländer und der Bund sich nicht über ihre Kompetenzen einig sind.
Links zum Bundesverfassungsgericht
- Website des Bundesverfassungsgerichts
- Deutschsprachiges Fallrecht - Urteile des Bundesverfassungsgerichts